Portal:Phoenicia/Sandbox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Phoenicia/Sandbox
THE PHOENICIA PORTAL
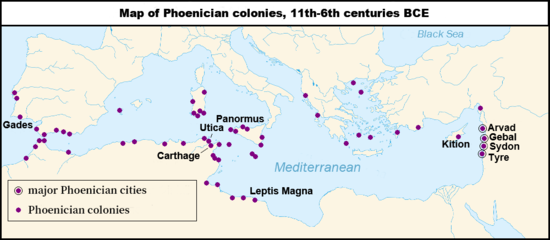
Phoenicia (/fəˈnɪʃə, fəˈniːʃə/), or Phœnicia, was an ancient Semitic thalassocratic civilization originating in the coastal strip of the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenicians expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel in modern Israel covering the entire coast of modern Lebanon. Beyond their homeland, the Phoenicians extended through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula.
The Phoenicians directly succeeded the Bronze Age Canaanites, continuing their cultural traditions following the decline of most major cultures in the Late Bronze Age collapse and into the Iron Age without interruption. It is believed that they self-identified as Canaanites and referred to their land as Canaan, indicating a continuous cultural and geographical association. The name Phoenicia is an ancient Greek exonym that did not correspond precisely to a cohesive culture or society as it would have been understood natively. Therefore, the division between Canaanites and Phoenicians around 1200 BC is regarded as a modern and artificial division.
The Phoenicians, known for their prowess in trade, seafaring and navigation, dominated commerce across classical antiquity and developed an expansive maritime trade network lasting over a millennium. This network facilitated cultural exchanges among major cradles of civilization like Greece, Egypt, and Mesopotamia. The Phoenicians established colonies and trading posts across the Mediterranean; Carthage, a settlement in northwest Africa, became a major civilization in its own right in the seventh century BC.
The Phoenicians were organized in city-states, similar to those of ancient Greece, of which the most notable were Tyre, Sidon, and Byblos. Each city-state was politically independent, and there is no evidence the Phoenicians viewed themselves as a single nationality. While most city-states were governed by some form of kingship, merchant families likely exercised influence through oligarchies. After reaching its zenith in the ninth century BC, the Phoenician civilization in the eastern Mediterranean gradually declined due to external influences and conquests. Yet, their presence persisted in the central and western Mediterranean until the destruction of Carthage in the mid-second century BC. — Read more about Phoenicia, its mythology and languagehttps://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Portal:Phoenicia/Sandbox&action=edit
Read or find an article
The Readers' FAQ and our about page contain the most commonly sought information about Wikipedia.
For simple searches, there is a search box at the top of every page. Type what you are looking for in the box. Partial matches will appear in a dropdown list. Select any page in the list to go to that page. Or, select the magnifying glass "Go" button, or press ↵ Enter, to go to a full search result. For advanced searches, see Help:Searching.
There are other ways to browse and explore Wikipedia articles; many can be found at Wikipedia:Contents. Also see our disclaimer for cautions about Wikipedia's limitations.
Edit an article
Contributing is easy: see how to edit a page. For a quick summary on participating, see contributing to Wikipedia, and for a friendly tutorial, see our introduction. For a listing of introductions and tutorials by topic, see getting started. The Simplified Manual of Style and Cheatsheet can remind you of basic wiki markup.
Be bold in improving articles! When adding facts, please provide references so others may verify them. If you are affiliated with the article subject, please see our conflict of interest guideline.
The simple guide to vandalism cleanup can help you undo malicious edits.
If you're looking for places you can help out, the Task Center is the place to go, or check out what else is happening at the community portal. You can practice editing and experiment in a sandboxyour sandbox.
,
 Featured article
-
Featured article
-
This is a Featured article, which represents some of the best content on English Wikipedia..
Volubilis (Latin pronunciation: [wɔˈɫuːbɪlɪs]; Arabic: وليلي, romanized: walīlī; Berber languages: ⵡⵍⵉⵍⵉ, romanized: wlili) is a partly-excavated Berber-Roman city in Morocco situated near the city of Meknes that may have been the capital of the Kingdom of Mauretania, at least from the time of King Juba II. Before Volubilis, the capital of the kingdom may have been at Gilda.
Built in a fertile agricultural area, it developed from the 3rd century BC onward as a Berber, then proto-Carthaginian, settlement before being the capital of the kingdom of Mauretania. It grew rapidly under Roman rule from the 1st century AD onward and expanded to cover about 42 hectares (100 acres) with a 2.6 km (1.6 mi) circuit of walls. The city gained a number of major public buildings in the 2nd century, including a basilica, temple and triumphal arch. Its prosperity, which was derived principally from olive growing, prompted the construction of many fine town-houses with large mosaic floors. (Full article...) Good article
-
Good article
-
This is a Good article, an article that meets a core set of high editorial standards.

The Battle of Ibera, also known as the Battle of Dertosa, was fought in the spring of 215 BC on the south bank of the Ebro River near the town of Ibera and was part of the Second Punic War. A Roman army, under the command of the brothers Gnaeus and Publius Scipio, defeated a similarly sized Carthaginian army under Hasdrubal Barca. The Romans, under Gnaeus Scipio, had invaded Iberia in late 218 BC and established a foothold after winning the Battle of Cissa. This lodgement, on the north-east Iberian coast, between the Ebro and the Pyrenees, blocked the route of any reinforcements from Iberia for the army of Hannibal, who had invaded Italy from Iberia earlier in the year. Hasdrubal attempted to evict the Romans in 217 BC, but this ended in defeat when the Carthaginian naval contingent was mauled at the Battle of Ebro River.
Hasdrubal spent the rest of 217 BC and all of 216 BC subduing rebellious indigenous Iberian tribes, largely in the south. Under pressure from Carthage to reinforce Hannibal, and having been strongly reinforced, Hasdrubal marched north again in early 215 BC. Meanwhile, Scipio, who had also been reinforced, and joined by his brother Publius, had crossed the Ebro to besiege the Carthaginian-aligned town of Ibera. Hasdrubal approached and offered battle, which the Scipios accepted. Both armies were of similar sizes, about 25,000 men. When they clashed, the centre of Hasdrubal's army – which consisted of locally recruited Iberians – fled without fighting. The Roman legions pushed through the gap, turned to each side against the remaining Carthaginian infantry and enveloped them. Both sides are reported to have suffered heavy casualties; the Carthaginians' may have been very heavy. The Carthaginian camp was sacked, but Hasdrubal escaped with most of his cavalry. (Full article...)Selected Phoenician inscriptions and language articles -
The Baalshillem Temple Boy, or Ba'al Sillem Temple Boy, is a votive statue of a "temple boy" with a Phoenician inscription known as KAI 281. It was found along with a number of other votive statues of children near the canal in the Temple of Eshmun in 1963-64 by Maurice Dunand, and is currently in the National Museum of Beirut.
The base of the statue was found separately; as late as 1974 Everett Mullen wrote that: "Only the base of the inscription was found; it has a large cavity at the top where the image of the squatting child would be expected on analogy with the other images which were found alongside this inscription."
The inscription mentions four previously unknown names of Kings of Sidon, which correspond exactly with those from known Sidonian coins. The inscription has been translated as follows:
This (is the) statue that Baalshillem, son of King Ba'na, king of the Sidonians, son of King Abdamun, king of the Sidonians, son of King Baalshillem, king of the Sidonians, gave to his lord Eshmun at the YDLL spring. May he bless him.
The inscription is dated from the end of the 5th century BCE. Nothing else is known about the kings mentioned in the inscription.
According to Josette Elayi, the statue represents Abdashtart I, who was the son of Baalshillem II. The statue is 35cm high. (Full article...)Selected Phoenician mythology articles -

General images
Categories
Related portals
Wikiproject
Other Wikimedia and Wikiportals
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Parent portal: Lebanon