Portal:Phoenicia
THE PHOENICIA PORTAL
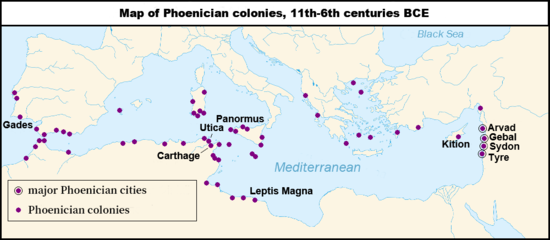
Phoenicia (/fəˈnɪʃə, fəˈniːʃə/), or Phœnicia, was an ancient Semitic thalassocratic civilization originating in the coastal strip of the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenicians expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel in modern Israel covering the entire coast of modern Lebanon. Beyond their homeland, the Phoenicians extended through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula.
The Phoenicians directly succeeded the Bronze Age Canaanites, continuing their cultural traditions following the decline of most major cultures in the Late Bronze Age collapse and into the Iron Age without interruption. It is believed that they self-identified as Canaanites and referred to their land as Canaan, indicating a continuous cultural and geographical association. The name Phoenicia is an ancient Greek exonym that did not correspond precisely to a cohesive culture or society as it would have been understood natively. Therefore, the division between Canaanites and Phoenicians around 1200 BC is regarded as a modern and artificial division.
The Phoenicians, known for their prowess in trade, seafaring and navigation, dominated commerce across classical antiquity and developed an expansive maritime trade network lasting over a millennium. This network facilitated cultural exchanges among major cradles of civilization like Greece, Egypt, and Mesopotamia. The Phoenicians established colonies and trading posts across the Mediterranean; Carthage, a settlement in northwest Africa, became a major civilization in its own right in the seventh century BC.
The Phoenicians were organized in city-states, similar to those of ancient Greece, of which the most notable were Tyre, Sidon, and Byblos. Each city-state was politically independent, and there is no evidence the Phoenicians viewed themselves as a single nationality. While most city-states were governed by some form of kingship, merchant families likely exercised influence through oligarchies. After reaching its zenith in the ninth century BC, the Phoenician civilization in the eastern Mediterranean gradually declined due to external influences and conquests. Yet, their presence persisted in the central and western Mediterranean until the destruction of Carthage in the mid-second century BC. — Read more about Phoenicia, its mythology and language
 Featured article
•
Featured article
•
A Featured article represents some of the best content on Wikipedia
The Mercenary War, also known as the Truceless War, was a mutiny by troops that were employed by Carthage at the end of the First Punic War (264–241 BC), supported by uprisings of African settlements revolting against Carthaginian control. It lasted from 241 to late 238 or early 237 BC and ended with Carthage suppressing both the mutiny and the revolt.
The war began in 241 BC as a dispute over the payment of wages owed to 20,000 foreign soldiers who had fought for Carthage in Sicily during the First Punic War. When a compromise seemed to have been reached, the army erupted into full-scale mutiny under the leadership of Spendius and Matho. 70,000 Africans from Carthage's oppressed dependent territories flocked to join them, bringing supplies and finance. War-weary Carthage fared poorly in the initial engagements of the war, especially under the generalship of Hanno. Hamilcar Barca, a veteran of the campaigns in Sicily (and father of Hannibal Barca), was given joint command of the army in 240 BC; and supreme command in 239 BC. He campaigned successfully, initially demonstrating leniency in an attempt to woo the rebels over. To prevent this, in 240 BC Spendius and Autaritus tortured 700 Carthaginian prisoners to death (including Gisco), after which the war was pursued with great brutality on both sides. (Full article...)Phoenician mythology •
Baal Marqod (in Greek alphabet: ΒΑΛ ΜΑΡΚΟΔ, in Latin alphabet: BALMARCOD, restored in Phoenician: 𐤁𐤏𐤋 𐤌𐤓𐤒𐤃, romanized: bʿl mrqd) was a Phoenician god of dancing. He is attested in Greek and Latin inscriptions from the Maronite monastery in Deir al-Qal'a (near Beit Mery), which was built on a sanctuary dedicated to Baal Marqod, built in the first century CE. Although 19th century scholar had made some different hypotheses of the nature of this god, he is commonly explained as "Baal of dancing" or "lord of dancing" (Baal is both a noun meaning "lord" and a divine name). The name is believed to correspond with his Greek title κοίρανος κωμων (κῶμοι implies games and dances). it is unknown whether he is called so because he was considered the creator of dancing or because dancing was merely the proper way to worship him.
The inscriptions often addressed him as "Iupiter Optimus Maximus Balmarcod" (not Jupiter Optimus Maximus Capitolinus). In one inscription he was called also Μηγριν, meaning threshing floor, as in Hebrew grn), and it may mean that Baal Marqod was also the protector of the crops. (Full article...)Images
 Good article
•
Good article
•
A Good article meets a core set of high editorial standards
Gisco was a Carthaginian general who served during the closing years of the First Punic War (264–241 BC) and took a leading part in the events which sparked the Mercenary War. He was a citizen of the city state of Carthage, which was located in what is now Tunisia. His date of birth and age at death are both unknown, as are his activities prior to his rise to prominence towards the end of the First Punic War.
When the Carthaginians conceded defeat in the war in 241 BC, Gisco was commander of the major base of Lilybaeum (modern Marsala) on Sicily, subordinate to Hamilcar Barca, the overall Carthaginian commander on the island. On being ordered to negotiate a peace treaty, Hamilcar retired to Carthage in a rage, leaving Gisco, as the next most senior commander, in charge of negotiations with the Romans. These resulted in the Treaty of Lutatius, which ended the war. By this time the troops whom he had sent from Sicily to Africa to be repatriated were in a mutinous state over a pay dispute, and Gisco, who had a good reputation with them, was hastily recalled to deal with the situation. The discontent seemed to have abated when, for some unknown reason, discipline broke down. Several soldiers insisted that no deal with Carthage was acceptable, a riot broke out and dissenters were stoned to death. Gisco and his staff were taken prisoner and his treasury was seized. (Full article...)Phoenician inscriptions & language •
The sarcophagus of Eshmunazar II is a 6th-century BC sarcophagus unearthed in 1855 in the grounds of an ancient necropolis southeast of the city of Sidon, in modern-day Lebanon, that contained the body of Eshmunazar II (Phoenician: 𐤀𐤔𐤌𐤍𐤏𐤆𐤓 ʾšmnʿzr, r. c. 539 – c. 525 BC), Phoenician King of Sidon. One of only three Ancient Egyptian sarcophagi found outside Egypt, with the other two belonging to Eshmunazar's father King Tabnit and to a woman, possibly Eshmunazar's mother Queen Amoashtart, it was likely carved in Egypt from local amphibolite, and captured as booty by the Sidonians during their participation in Cambyses II's conquest of Egypt in 525 BC. The sarcophagus has two sets of Phoenician inscriptions, one on its lid and a partial copy of it on the sarcophagus trough, around the curvature of the head. The lid inscription was of great significance upon its discovery as it was the first Phoenician language inscription to be discovered in Phoenicia proper and the most detailed Phoenician text ever found anywhere up to that point, and is today the second longest extant Phoenician inscription, after the Karatepe bilingual.
The sarcophagus was discovered by Alphonse Durighello, a diplomatic agent in Sidon engaged by Aimé Péretié, the chancellor of the French consulate in Beirut. The sarcophagus was sold to Honoré de Luynes, a wealthy French nobleman and scholar, and was subsequently removed to the Louvre after the resolution of a legal dispute over its ownership.
More than a dozen scholars across Europe and the United States rushed to translate the sarcophagus inscriptions after its discovery, many noting the similarities between the Phoenician language and Hebrew. The translation allowed scholars to identify the king buried inside, his lineage, and his construction feats. The inscriptions warn against disturbing Eshmunazar II's place of repose; it also recounts that the "Lord of Kings", the Achaemenid king, granted Eshmunazar II the territories of Dor, Joppa, and Dagon in recognition for his services.
The discovery led to great enthusiasm for archaeological research in the region and was the primary reason for Renan's 1860–1861 Mission de Phénicie, the first major archaeological mission to Lebanon and Syria. Today, it remains one of the highlights of the Louvre's Phoenician collection. (Full article...)Did you know (auto-generated) •

- ... that Bochart's 1646 Geographia Sacra seu Phaleg et Canaan was the first full-length book devoted to the Phoenicians?
- ... that the deity of the Phoenician sanctuary of Kharayeb remains unidentified due to the absence of names of specific gods in unearthed inscriptions?
- ... that Eshmunazar I, the Phoenician king of Sidon, participated in the Neo-Babylonian campaigns against Egypt, where he seized stone sarcophagi belonging to members of the Egyptian elite?
- ... that the discovery of Phoenician metal bowls in 1849 created the entire concept of Phoenician art?
- ... that the sarcophagus of Eshmunazar II, the Phoenician king of Sidon, is one of only three ancient Egyptian sarcophagi unearthed outside Egypt?
- ... that alongside a 7th-century BC Phoenician shipwreck, two additional wrecks from various historical periods were unearthed in Bajo de la Campana, situated off the coast of Cartagena, Spain?
Related portals
Categories
Wikiproject
Other Wikimedia and Wikiportals
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Parent portal: Lebanon