User:KYPark/Sandbox
Reading the 1955 paper* once again reminds me of the inspiration that the concept had from my early interest in encyclopaedism. In 1970,** Manfred Kochen commented on its role in the worldwide encyclopaedic movement.13 Today the Internet has enabled the development of Wikipedia and other grand schemes that will make the H.G. Wells dream of a World Brain a reality.
- Footnote
- 13. Kochen M. WISE -- world information synthesis and encyclopedia. J Document, 1972; 28: 322-343.
- My footnotes
- * Eugene Garfield. Citation indexes for science: a new dimension in documentation through association of ideas. Science, 1955; 122: 108-11. [2]
- ** "1970" may be mistaken for 1972.
Reading the 1955 paper* once again reminds me of the inspiration that the concept had from my early interest in encyclopaedism. In 1970,** Manfred Kochen commented on its role in the worldwide encyclopaedic movement.13 Today the Internet has enabled the development of Wikipedia and other grand schemes that will make the H.G. Wells dream of a World Brain a reality.
- Footnote
- 13. Kochen M. WISE -- world information synthesis and encyclopedia. J Document, 1972; 28: 322-343.
- My footnotes
- * Eugene Garfield. Citation indexes for science: a new dimension in documentation through association of ideas. Science, 1955; 122: 108-11. [4]
- ** "1970" may be mistaken for 1972.
Figures and Tables[edit]
Table 1[edit]
| Citation | Abstract | First paragraph |
Last paragraph |
First & Last paragraph | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transmitted correct information (bits/document) |
.0953 | .1233 | .1603 | .1659 | .3013 |
Table 2[edit]
| denotation : an act or process of denoting; MEANING, esp a direct specific meaning as distinct from connotations; NAME, SIGN, INDICATION. | connotation : the suggesting of a meaning but a word apart from the thing it explicitly names or describes; something suggested by a word or thing, IMPLICATION; the signification of something. |
| denote : to serve as an indication, BETOKEN; to serve as an arbitrary mark for; to make known, ANNOUNCE; to serve as a linguistic expression of the motion of, MEAN. | connote : to convey in addition to exact explicit meaning; to be associated with or inseparable from as a consequence or concomitant. |
| explicit : free from all vagueness and ambiguity, fully developed or formulated; unreserved and unambiguous in expression; externally visible. | implicit : capable of being understood from something else through unexpected, IMPLIED; involved in the nature or essence of something though not revealed, expressed or developed; POTENTIAL. |
| extensional : of, relating to, or marked by extension, specif: DENOTATIVE; concerned with objective reality. | intensional : adj intension (1: INTENSIITY 2: CONNOTATAION). |
|
syn DENOTE, CONNOTE shared meaning element : to mean. In spite of this shared element of meaning, these terms are complementary rather than strictly synonymous and cannot be interchanged without significant loss of precision. DENOTE applies to the definitive meaning content of a term: in a noun, the thing or the definable class of things or ideas which it names; in a verb, the act or state which is affirmed. CONNOTE applies to the ideas or associations that are added to a term and cling to it, often as a result of personal experience but sometimes as a result of something extraneous (as a widely known context or connection with a widely known event). "Home," for example, denotes the place where one lives, but to one person it may connote comforts, intimacy, and affection and to another misery, estrangement, and abuse. | |
Figure 1[edit]
Figure 2[edit]
Figure 3[edit]
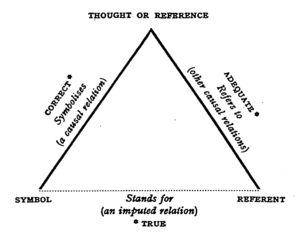
Figure 4[edit]
Figure 5[edit]
Figure 6[edit]
Figure 7[edit]
Figure 8[edit]
Figure 9[edit]
The analytic independent-particle model(IPM) has proved successful in describing both the ground1 and excited2,3 states of neutral atoms as well as ions.4 Furthermore, the method has been successfully used to obtain differential elastic cross sections for electrons on the rare gases.5-7 The IPM is particularly well suited for describing inelastic atomic processes also, and the reader should consult Green8 for a review of these meth- ods. |
Figure 10[edit]
- independent-particle model; ground state, neutral atom.
- independent-particle model; excited state, neutral atom.
- independent-particle model; excited state, neutral atom.
- independent-particle model; ground, excited state, ion.
- independent-particle model; differential elastic cross section, electron, rare gas.
- independent-particle model; differential elastic cross section, electron, rare gas.
- independent-particle model; differential elastic cross section, electron, rare gas.
- independent-particle model; inelastic atomic process; review.
Figure 11[edit]
- independent-particle model; ground state, neutral atom; oxygen;
- independent-particle model; excited state, neutral atom; oxygen; weighting, outer level; differential, total cross section;
- independent-particle model; excited state, neutral atom;
- independent-particle model; ground, excited state, ion; potential, electron; minimization, total energy;
- independent-particle model; differential elastic cross section, electron, rare gas.
- independent-particle model; differential elastic cross section, electron, rare gas.
- independent-particle model; differential elastic cross section, electron, rare gas.
- independent-particle model; inelastic atomic process; review;
- momentum transfer, cross section, neutral, ionized oxygen; electron gas cooling, calculation;
- total cross section, low energy;
- total cross section, low energy;
- phenomenological calculation, low energy scattering; polarization, potential, energy eigenvalue, outer electron, electron affinity; effective range expansion; modification;
- phenomenological calculation, low energy scattering; polarization, potential, energy eigenvalue, outer electron, electron affinity;
- phenomenological calculation, low energy scattering; polarization, potential, energy eigenvalue, outer electron, electron affinity; effective range expansion; modification;
- phenomenological calculation, low energy scattering; polarization, potential, energy eigenvalue, outer electron, electron affinity;
- elastic scattering calculation, oxygen; polarized orbital;
- elastic scattering calculation, oxygen; polarized orbital;
- elastic scattering calculation, oxygen; close coupling;
- elastic scattering calculation, oxygen; polarized orbital; close coupling;
- high energy calculation, Hartree Fock, static atom; Born approximation;
- total cross section, low energy; electron oxygen parameter;
- minimization, total energy;
- potential, elastic scattering; low energy, phase shift, electron;
- experimental level; excited state;
- experimental level; electron spectroscopy, chemical analysis;
- rare gas;
- weighting, outer level, energy;
- expansion, optical, potential, elastic scattering;
- -
- -
- single particle energy;
- modified, Born approximation, scattering amplitude;
- measurement, ratio, forward, back scattering;
- effective range expansion; modification;
- differential, total cross section;
- -
- negative ion, decay, quasistationary state;
Figure 12[edit]
| INDEX TERM | REFERENCE NUMBER |
|---|---|
| independent-particle model; | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 |
| ground state, neutral atom; | 1 |
| excited state, neutral atom; | 2, 3 |
| ground, excited state, ion; | 4 |
| differential elastic cross section, electron, rare gas; | 5, 6, 7 |
| inelastic atomic process, review; | 8 |
| momentum transfer, cross section, neutral, ionized oxygen, electron gas cooling calculation; | 9 |
| total cross section, low energy; | 10, 11, 21 |
| phenomenological calculation, low energy scattering; | 12, 13, 14, 15 |
| elastic scattering calculation, oxygen; | 16, 17, 18, 19 |
| polarized orbital; | 16, 17, 19 |
| close coupling; | 18, 19 |
| high energy calculation, Hartree Fock, static atom; | 20 |
| electron oxygen parameter; | 21 |
| independent-particle model, potential, electron, ion; | 4 |
| minimization, total energy; | 4, 22 |
| potential, elastic scattering; | 23 |
| experimental level; | 24, 25 |
| excited state; | 24, 2 |
| electron spectroscopy, chemical analysis; | 25 |
| oxygen; | 2, 1 |
| rare gas; | 26 |
| weighting, outer level, energy; | 27, 2 |
| expansion, optical, potential, elastic scattering; | 28 |
| polarization, potential, energy eigenvalue, outer electron, electron affinity; | 12, 13, 14, 15 |
| single particle energy; | 31 |
| modified, Born approximation, scattering amplitude; | 32 |
| measurement, ratio, forward, back scattering; | 33 |
| effective range expansion; | 13, 34, 14 |
| modification; | 34, 14 |
| differential, total cross section; | 35, 2 |
| Hartree Fock, Born approximation; | 20 |
| low energy, phase shift, electron; | 23 |
| negative ion, decay, quasistationary state; | 37 |
Figure 13[edit]
Figure 14[edit]
Figure 15[edit]
math examples[edit]
,
for .

![{\displaystyle V(r)=(-2/r)[(Z-\eta )\Omega +\eta ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0f1236678abd2bb3081797d9b54ce7816c01f430)
![{\displaystyle V_{p}=-(\alpha /r^{4})[1-c^{-(r/r_{p})^{8}}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5501fadf038fde657f1f323b4b019995a150990b)

![{\displaystyle \Delta _{l}={\frac {\alpha }{2kr_{m}}}[{\frac {1}{3}}+{\frac {1}{r_{m}^{2}}}({\frac {l(l+1)-2}{10k^{2}}}-{\frac {8r_{p}^{2}}{15}})]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ba38c711757bcb7c5f513ca2cc56b301421144fc)
