Portal:Devonian
The Devonian Portal
The Devonian (/dɪˈvoʊni.ən, dɛ-/ də-VOH-nee-ən, deh-) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era during the Phanerozoic eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at 419.2 million years ago (Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding Carboniferous period at 358.9 Ma. It is named after Devon, South West England, where rocks from this period were first studied.
The first significant evolutionary radiation of life on land occurred during the Devonian, as free-sporing land plants (pteridophytes) began to spread across dry land, forming extensive coal forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of vascular plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants (pteridospermatophytes) appeared. This rapid evolution and colonization process, which had begun during the Silurian, is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution. The earliest land animals, predominantly arthropods such as myriapods, arachnids and hexapods, also became well-established early in this period, after beginning their colonization of land at least from the Ordovician period.
Fishes, especially jawed fish, reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The armored placoderms began dominating almost every known aquatic environment. In the oceans, cartilaginous fishes such as primitive sharks became more numerous than in the Silurian and Late Ordovician. Tetrapodomorphs, which include the ancestors of all four-limbed vertebrates (i.e. tetrapods), began diverging from freshwater lobe-finned fish as their more robust and muscled pectoral and pelvic fins gradually evolved into forelimbs and hindlimbs, though they were not fully established for life on land until the Late Carboniferous. (Full article...)
Selected Devonian Article
Dunkleosteus is an extinct genus of large arthrodire ("jointed-neck") fish that existed during the Late Devonian period, about 382–358 million years ago. It was a pelagic fish inhabiting open waters, and one of the first apex predators of any ecosystem.
Dunkleosteus consists of ten species, some of which are among the largest placoderms ("plate-skinned") to have ever lived: D. terrelli, D. belgicus, D. denisoni, D. marsaisi, D. magnificus, D. missouriensis, D. newberryi, D. amblyodoratus, D. raveri, and D. tuderensis. The largest and best known species is D. terrelli. Since body shape is not known, various methods of estimation put the living total length of the largest known specimen between 4.1 to 10 m (13 to 33 ft) long and weigh around 1–4 t (1.1–4.4 short tons). However, lengths of 5 metres (16 ft) or more are poorly supported and the most extensive analyses support smaller size estimates.
Dunkleosteus could quickly open and close its jaw, creating suction like modern-day suction feeders, and had a bite force that is considered the highest of any living or fossil fish, and among the highest of any animal. Fossils of Dunkleosteus have been found in North America, Poland, Belgium, and Morocco. (Full article...)List of selected Devonian articles
|
|---|
Selected Devonian land plant article
List of selected Devonian articles
|
|---|
Selected Devonian formation
List of selected Devonian formation articles
|
|---|
Selected Devonian fish article
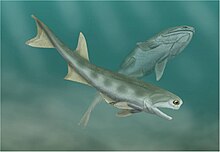
Cheirolepis (from Greek: χείρ kheír, 'hand' and Greek: λεπίς lepis 'scale') is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish that lived in the Devonian period of Europe and North America. It is the only genus yet known within the family Cheirolepidae and the order Cheirolepiformes. It was among the most basal of the Devonian actinopterygians and is considered the first to possess the "standard" dermal cranial bones seen in later actinopterygians.
Cheirolepis was a predatory freshwater and estuarine animal about 55 centimetres (22 in) long. It had a streamlined body with small, triangular ganoid scales similar to those of the Acanthodii. These scales had a basic structure typical of many early osteichthyans, with a superficial of ganoine overlying dentine, and a basal plate of bone. Cheirolepis had well-developed fins which gave it speed and stability, and was probably an active predator. Based on the size of its eyes, it hunted by sight. Cheirolepiss jaws, lined with sharp teeth, could be opened very wide, allowing it to swallow prey two thirds of its own size. ('Full article...)Selected Devonian invertebrate
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary colonies. Typically about 0.5 millimetres (1⁄64 in) long, they have a special feeding structure called a lophophore, a "crown" of tentacles used for filter feeding. Most marine bryozoans live in tropical waters, but a few are found in oceanic trenches and polar waters. The bryozoans are classified as the marine bryozoans (Stenolaemata), freshwater bryozoans (Phylactolaemata), and mostly-marine bryozoans (Gymnolaemata), a few members of which prefer brackish water. 5,869 living species are known. Originally all of the crown group Bryozoa were colonial, but as an adaptation to a mesopsammal (interstitial spaces in marine sand) life or to deep‐sea habitats, secondarily solitary forms have since evolved. Solitary species has been described in four genera; Aethozooides, Aethozoon, Franzenella and Monobryozoon). The latter having a statocyst‐like organ with a supposed excretory function.
The terms Polyzoa and Bryozoa were introduced in 1830 and 1831, respectively. Soon after it was named, another group of animals was discovered whose filtering mechanism looked similar, so it was included in Bryozoa until 1869, when the two groups were noted to be very different internally. The new group was given the name "Entoprocta", while the original Bryozoa were called "Ectoprocta". Disagreements about terminology persisted well into the 20th century, but "Bryozoa" is now the generally accepted term.
Colonies take a variety of forms, including fans, bushes and sheets. Single animals, called zooids, live throughout the colony and are not fully independent. These individuals can have unique and diverse functions. All colonies have "autozooids", which are responsible for feeding, excretion, and supplying nutrients to the colony through diverse channels. Some classes have specialist zooids like hatcheries for fertilized eggs, colonial defence structures, and root-like attachment structures. Cheilostomata is the most diverse order of bryozoan, possibly because its members have the widest range of specialist zooids. They have mineralized exoskeletons and form single-layered sheets which encrust over surfaces, and some colonies can creep very slowly by using spiny defensive zooids as legs. (Full article...)List of selected Devonian invertebrates articles
|
|---|
Need help?
Do you have a question about Devonian that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
Subcategories
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



























