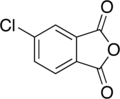
4-Chlorophthalic anhydride
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-Chloro-2-benzofuran-1,3-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.866 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H3ClO3 | |
| Molar mass | 182.56 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | ~99 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
4-Chlorophthalic anhydride is a monochlorinated aromatic anhydride. It is an isomer of 3-chlorophthalic anhydride and a derivative of phthalic anhydride.
Properties[edit]
It has a melting point of around 99 °C. Like most acid anhydrides, it can hydrolyze in the presence of water.
Production[edit]
It can be produced by chlorination of phthalic anhydride.
Applications[edit]
It may be used to produce herbicides and pesticides, intermediates for active pharmaceutical ingredients and can be used as a monomer for the production of polyimides.
References[edit]
- Chlorination of phthalic anhydride http://www.freepatentsonline.com/4297283.html
