Oropendola
| Oropendola | |
|---|---|

| |
| Montezuma oropendola (Psarocolius montezuma) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Icteridae |
| Genus: | Psarocolius Wagler, 1827 |
| Type species | |
| Oriolus cristatus[1] Gmelin, 1788
| |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Oropendolas are a genus of passerine birds, Psarocolius, in the New World blackbird family Icteridae. They were formerly split among two or three different genera and are found in Central and South America.
All the oropendolas are large birds with pointed bills, and long tails which are always at least partially bright yellow. Males are usually larger than females.
The plumage is typically chestnut, dark brown or black, although the Green oropendola and olive oropendola have, as their names imply, an olive coloration to the head, breast and upper back. The legs are dark, but the bill is usually a strikingly contrasting feature, either pale yellow, or red-tipped with a green or black base. In several species there is also a blue or pink bare cheek patch.
Oropendolas are birds associated with forests or, for a few species, more open woodland. They are colonial breeders, with several long woven basket nests in a tree, each hanging from the end of a branch.
These gregarious birds eat large insects and fruit. They are very vocal, producing a wide range of songs and calls, sometimes including mimicry.
Systematics[edit]

The following species are recognised in the genus Psarocolius:
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black oropendola | Psarocolius guatimozinus (Bonaparte, 1853) |
northwestern Colombia and the extreme southeastern part of Panama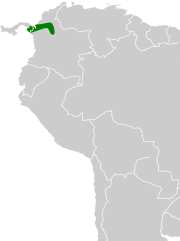
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Chestnut-headed oropendola | Psarocolius wagleri (Gray, GR,, 1844) Two subspecies
|
the Caribbean coastal lowlands from southern Mexico to central Costa Rica, both slopes of southern Costa Rica and Panama, and the Pacific lowlands of Colombia and north-eastern Ecuador.
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Russet-backed oropendola | Psarocolius angustifrons (Spix, 1824) Seven subspecies
|
Venezuela, Colombia, Brazil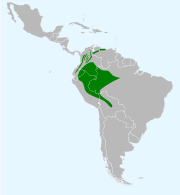
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Dusky-green oropendola | Psarocolius atrovirens (Lafresnaye & D'Orbigny, 1838) |
Peru (Huánuco) to Bolivia(Santa Cruz)
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Green oropendola | Psarocolius viridis (Müller, 1776) |
Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, Surinam, French Guiana, Brazil, Ecuador, Bolivia and Peru
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Crested oropendola | Psarocolius decumanus (Pallas, 1769) Four subspecies
|
from Panama and Colombia south to northern Argentina, as well as on Trinidad and Tobago
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
Former species[edit]
Four species of oropendola were formerly classified within the genus Gymnostinops; alternatively, the crested oropendola (and possibly others) would have also been placed here (Price & Lanyon 2002):
- Montezuma oropendola (Psarocolius montezuma)
- Baudo oropendola (Psarocolius cassini)
- Olive oropendola (Psarocolius bifasciatus)
Price & Lanyon (2002) used mtDNA cytochrome b and NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2 sequence data to research oropendola phylogeny. As can be observed from morphology, the band-tailed (Ocyalus latirostris) and the casqued oropendolas (Psarocolius oseryi) are the most distinct species. Genetically, they appear to be more closely related to the caciques, and both species would be classified in the genus Ocyalus. Furthermore, the casqued oropendola could be separated into Clypicterus, forming what would then become a monotypic genus (like Ocyalus).
References[edit]
- ^ "Icteridae". aviansystematics.org. The Trust for Avian Systematics. Retrieved 2023-07-16.
- ffrench, Richard; O'Neill, John Patton & Eckelberry, Don R. (1991): A guide to the birds of Trinidad and Tobago (2nd edition). Comstock Publishing, Ithaca, N.Y.. ISBN 0-8014-9792-2
- Hilty, Steven L. (2003): Birds of Venezuela. Christopher Helm, London. ISBN 0-7136-6418-5
- Jaramillo, Alvaro & Burke, Peter (1999): New World Blackbirds. Christopher Helm, London. ISBN 0-7136-4333-1
- Price, J. Jordan & Lanyon, Scott M. (April 2002). "A robust phylogeny of the oropendolas: Polyphyly revealed by mitochondrial sequence data" (PDF). Auk. 119 (2): 335–348. doi:10.1642/0004-8038(2002)119[0335:arpoto]2.0.co;2.
- Stiles, F. Gary & Skutch, Alexander Frank (1989): A guide to the birds of Costa Rica. Comistock, Ithaca. ISBN 0-8014-9600-4
External links[edit]
- Oropendola videos, photos and sounds - Internet Bird Collection






